Social Welfare in Spain
Sometime in your life you may be in need of the support provided by social security benefits. The Social Welfare system in Spain provides benefits relaying on different administrations.
The first step is to register at the City Hall census (padrón). Asocial worker (trabajador social) will inform you of the services provided by the social welfare (servicios sociales / bienestar social).
Type of service by administration
Local City Hall
Ayuntamiento
Food banks, meals services
Remote assistance, alarm system
Homecare / Elder’s homes
Regional Office
Gobierno Comunidad Autónoma
Minimum Living Income allowance
Minimum income benefits programmes
Social housing
National Office
Seguridad Social / Bienestar Social
Minimum Living Income
Non-contributory pensions
Unemployment benefit
Welfare State four pillars
The four pillars that make up the Welfare State are:
Some minimum income
Non-contributory pensions by Pensions system
Economic benefits granted to citizens in a situation of protectable need and who do not have sufficient resources for subsistence under the legally established terms, even if they have never contributed or not for the time needed to reach contributory benefit level.
Minimum Vital Income by Social assistance system
The Minimum Living Allowance is a benefit aimed at preventing the risk of poverty and social exclusion of people living alone or who are part of a cohabitation unit and lacking the basic economic resources to meet their basic needs.
This Minimum Living Allowance (Ingreso Mínimo Vital, IMV) is defined as a subjective right to an economic benefit, which is part of the protective action of the Social Security, and guarantees a minimum level of income for people in a situation of economic vulnerability. The system seeks to ensure a real improvement in opportunities for social and employment inclusion for the recipients.
It operates as a protection network aimed at allowing transit from a situation of exclusion to participation in society. It design will contain incentives for employment and inclusion, based on different forms of cooperation between administrations.
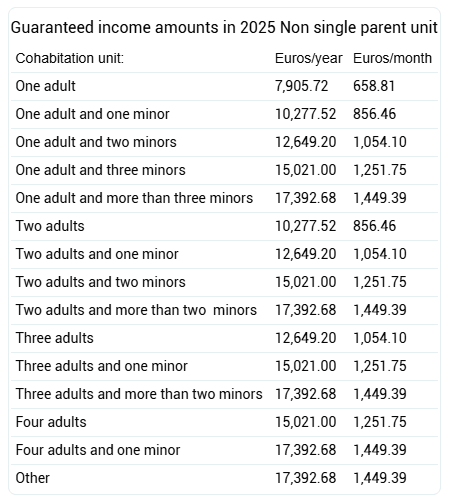
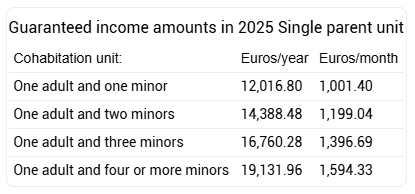
Monthly guaranteed income amount in 2025
- For an individual beneficiary: 100% of the annual sum of non-contributory pensions divided by 12. In 2025, 658.81 euros. This amount is increased by 22% if the recipient has a degree of disability equal to or greater than 65%.
- For the cohabitation unit, the above amount increased by 30% for additional members as of the second member, with a maximum of 220%

Social Assistance: servicios sociales, bienestar social
Social services are the professional social intervention services that public administrations make available to citizens to respond to situations of special need. This service may be called “Servicios sociales” or “Bienestar social”.
Social services include, for example,
- care for the dependent elderly and disabled,
- family protection and care for children growing up away from their families,
- support in critical situations such as gender-based violence, homelessness, addiction, or loss of income.
Likewise, social services work with the community to make it more inclusive, cohesive, and participatory.
In Spain, social services are the responsibility of the Autonomous Communities, and the first and closest care for individuals is provided by municipalities through primary social care. If you want to know the contact information for the primary social care center closest to your home, please contact your local council.
Who is in charge
Central level (State) establishes the general regulatory framework and strategic guidelines for social services, while Autonomous Communities have primary responsibility for their development, management, and provision. Municipalities provide the primary social care closest to citizens, acting as the first gateway to social services through basic social service centers.
National
Establishes basic legislation and general policies regarding social welfare.
Defines social rights and economic benefits guaranteed at the national level.
Coordinates social policies and oversees their compliance by the Autonomous Communities.
Autonomous Communities
Develop and manage social services in their territories.
They are responsible for planning and implementing most social service policies.
They establish the services and benefits offered within their territories.
Municipalities
Responsible for basic social care.
They manage social service centers, which are the gateway for information, guidance, and support for citizens.
They may have powers delegated by the State or the Autonomous Communities for the direct provision of services.
